Description
PROFILE
THE LARGEST AND SMALLEST SIZE THAT CAN BE PRODUCED FOR ALUMINUM SIZE
the maximum diagonal is 500mm, and the minimum is about 10*10.
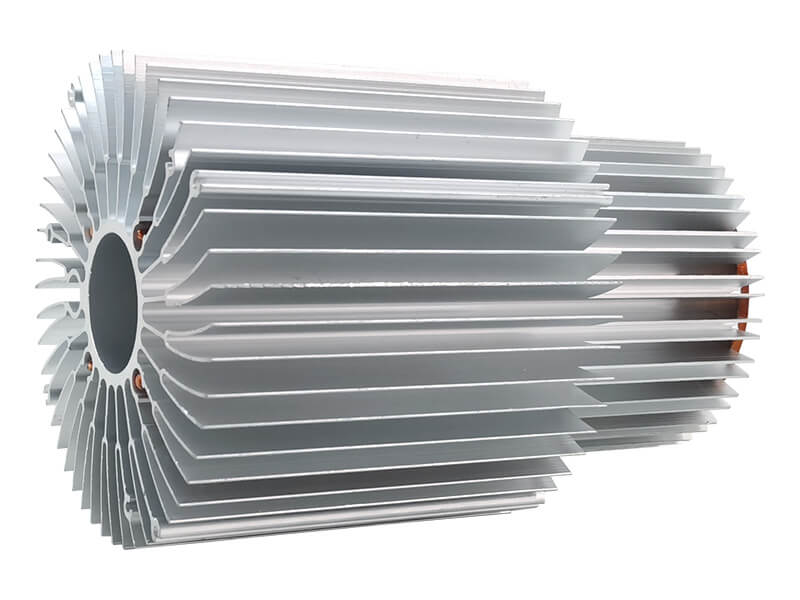

CLASSIFIED BY PRODUCTION METHOD
According to the production method, profiles can be divided into hot-rolled profiles, cold-formed profiles, cold-rolled profiles, cold-drawn profiles, extruded profiles, forged profiles, hot-bent profiles, welded profiles and special rolled profiles.
CLASSIFIED BY SECTION CHARACTERISTICS
Profiles can be divided into simple cross-sectional profiles and complex cross-sectional profiles according to their cross-sectional shapes. Simple cross-section profiles are symmetrical in cross-section, relatively uniform and simple in shape, such as round steel, wire, square steel, and steel. Complex cross-section profiles are also called special-shaped cross-section profiles, which are characterized by obvious convex-concave branches on the cross-section. Therefore, it can be further divided into flange profiles, multi-step profiles, wide and thin profiles, locally specially processed profiles, irregular curved profiles, composite profiles, periodic cross-section profiles, metal wires, and so on.
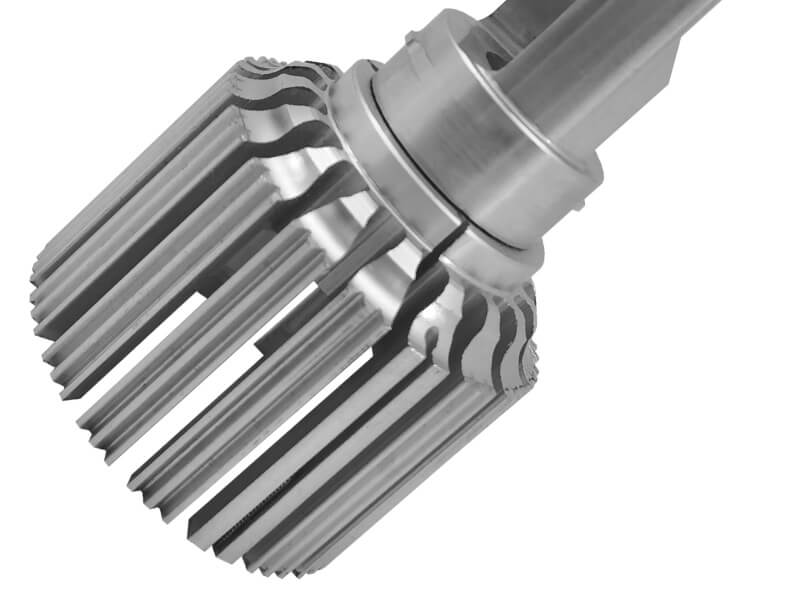

CLASSIFIED BY DEPARTMENT OF USE
The profiles are classified into railway profiles (rails, fishplates, rails for turnouts, wheels, tyres), automotive profiles (rims, tire retainers and lock rings), and shipbuilding profiles (L-shaped steel, flat ball steel). , Z-shaped steel, marine window frame steel), structural and construction profiles (H-shaped steel, I-beam, channel steel, angle steel, crane rails, window and door frame materials, steel sheet piles, etc.), mining steel (U-shaped steel, Channel steel, mining I-beam, scraper steel, etc.), profiled materials for machinery manufacturing, etc.
CLASSIFIED BY SECTION SIZE
Profiles can be divided into large, medium and small profiles according to their cross-sectional dimensions, and their classification is often classified as they are suitable for rolling on large, medium and small rolling mills. The distinction between large, medium and small is actually not strict. In addition, there is a method of distinguishing by unit weight (kg/m). It is generally believed that those with a unit weight of less than 5 kg/m are small-sized materials, those with a unit weight of 5-20 kg/m are medium-sized materials, and those with a unit weight of more than 20 kg/m are large-sized materials.
CONTACT US
Our team is on hand to address your concerns.
Just complete the email form below.
Thank You!

